What is bookkeeping?
Bookkeeping is the systematic routine method of retrieving financial information categorizing that information and putting it into an accounting system and generating reports that are then used by decision maker to make better financial decisions in the future.
Bookkeeping is the recording of past financial data so that you can make future business decisions.
This article guide you about how do beginners learn bookkeeping.
How can you perform the bookkeeping duties for your small business?
It takes is a simple six step bookkeeping process
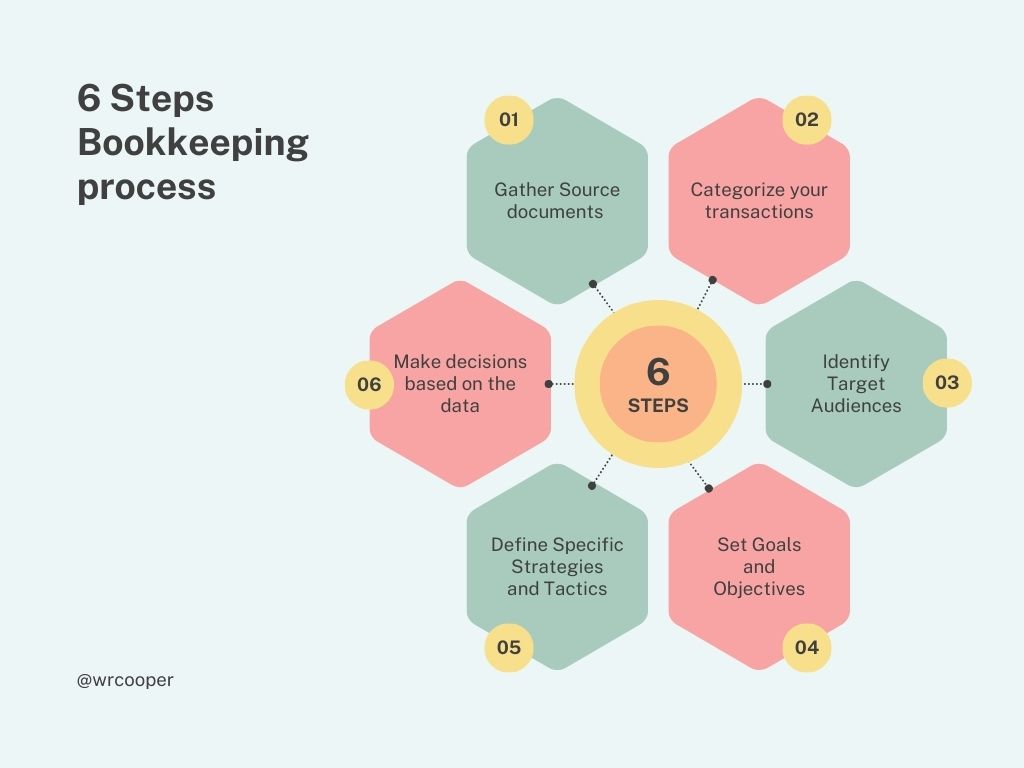
Step 1: Gather Source documents
Source documents are original records for a transaction thing. For example, an invoice a sales order or receipt. All of these documents have a date a buyer and a seller an amount and the product or service that was provided. Most people don’t keep physical copies of their source documents instead they rely on bank statements to tell the story.
In most cases bank or credit card statements have all the information needed to substantiate a transaction but keep in mind that cash transactions are not recognizable using bank statements alone and if you have a cash transaction you have to retain the physical receipt or recall the purpose of the transaction to correctly classify those types of transactions. So as a tip it’s good practice to use a debit card or a credit card to make and receive all payments this way you or your bookkeeper can rely mostly on your bank statements to classify transactions making step one extremely easy.
Step 2: Categorize your transactions
Classifying your transactions into a specific category is the core of the bookkeeping process and there are five main categories that transactions can fall into.
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Equity
- Revenue
- Expenses
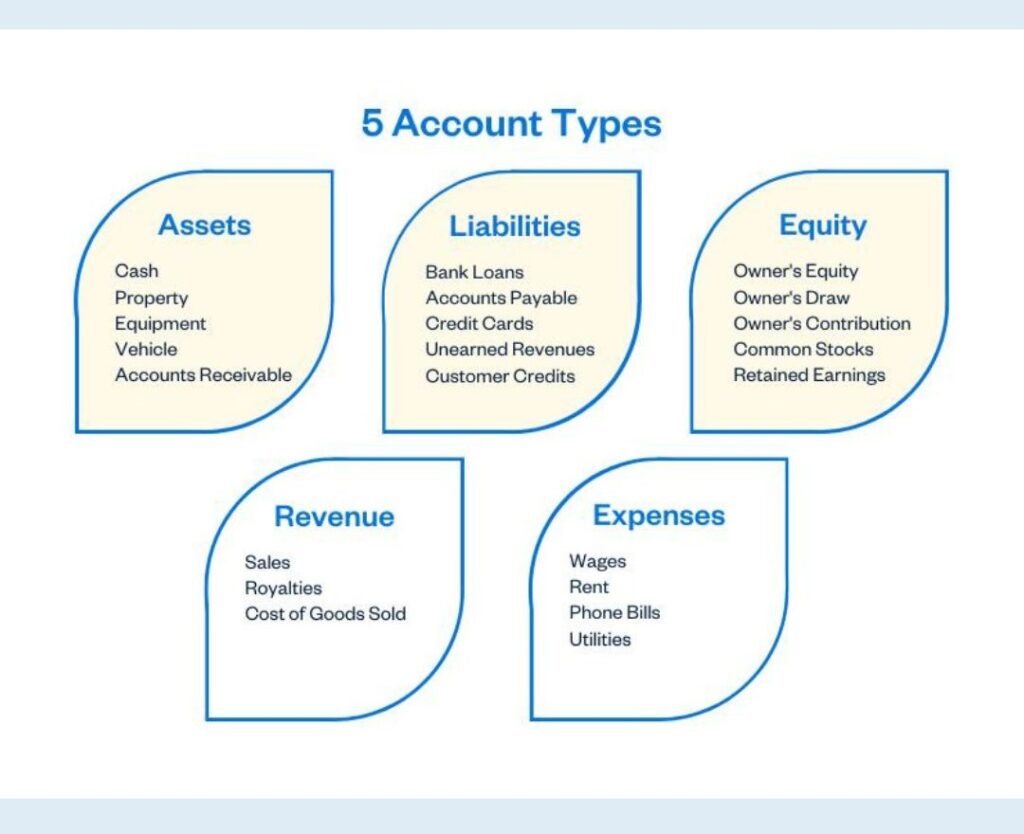
Each of these categories can be broken down into further subcategories like a subcategory for inventory story under assets. The first step in categorizing is to identify which category a transaction belongs to like cash would be an asset, future obligations like payroll or a loan would be considered a liability.
Equity increases with revenue and capital contributions and Equity is decreased with distributions and expenses the sale of products or Services would be considered revenue and the cost to generate that Revenue would be considered expenses. So to help with the organization in categorizing of transactions I would recommend you use a software like QuickBooks.
Step 3: Reconcile your transactions
A great bookkeeper will reconcile their transactions to make sure each and every transaction is accounted for. This idea of reconciling is actually pretty simple. It’s the process of matching all of your transactions that are on your bank statement to what’s in your accounting software and when you’re dealing with hundreds and thousands of transactions it can be pretty easy to double count a transaction or two or simply miss one.
Reconciling helps catch all errors. You start with the beginning balance on your statements which should match what’s in your accounting software and then check the line by line to make sure every transaction is accounted for.
Step 4: Prepare financial statements
The process of adding, classifying and reconciling your transactions provide the input for financial statements. There are three main financial statements that should be prepared
- Balance sheet
- Income statement
- Cash flow statement
Balance sheet is also known as a statement of financial position it contains assets liabilities and Equity transactions. The assets on the balance sheet must equal liabilities plus Equity. If not, your balance sheet is out of balance.
Income statement is also known as your profit and loss statement or P & L Statement for short. It contains your revenue and expenses. The income statement simply tells you how profitable you are at any given period.
Now, your cash flow statement has three components:
- Cash from operations
- Cash from financing
- Cash from investments.
The cash flow statement shows how transactions from the balance sheet affect your cash account. Alright, let’s move on to the last two steps.
Step 5: Read your financial statements
So, you prepared those financial statements. Now what most businesses fail or succeed based on their financial statements; therefore, it’s critical that you review your financial statements, understand your financial statements, and take advantage of the insight they provide.
This key action is the difference between you having a more profitable business this year than you had last year. In order to read your financial statements, you should understand how they’re structured.
So, let’s look at the structure of a balance sheet. Remember a balance sheet must balance. Assets are listed first, and liabilities and equities are listed last.
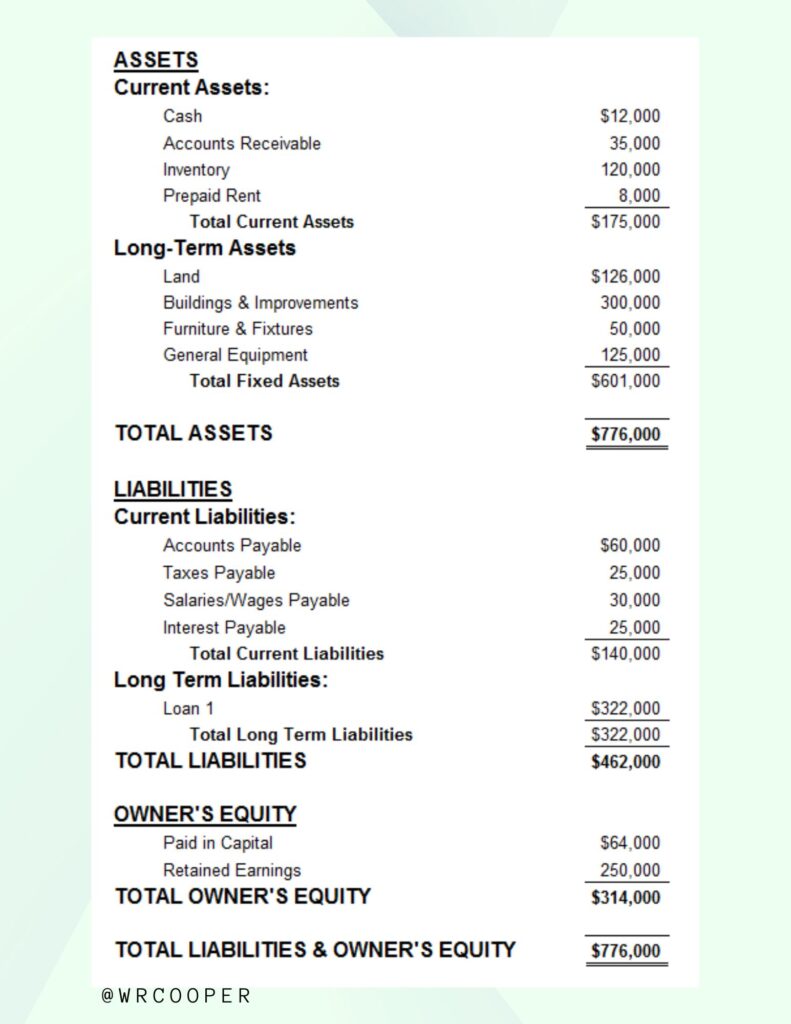
Now, assets are ordered in terms of liquidity or how long it will take for that asset to convert into cash. For this reason, cash is always the first thing listed under assets. Cash is the first thing you will see on a balance sheet, followed by other current assets like accounts receivable and inventory. Long-term assets are listed after current assets, and fixed assets like equipment take into consideration depreciation, something called a contra asset that would reduce the asset side of the balance sheet. You can think of depreciation as the amount of an asset that has been used up.
Now, the liabilities section is listed similar to assets, where current liabilities show before long-term liabilities. Current liabilities are debts due within 12 months. Common accounts listed under liabilities are accounts payable, wages payable, and credit cards. Common accounts listed under long-term liabilities are things like bank loans, car loans, and capital leases.
The equity section is listed last on the balance sheet. It shows the ownership in a business and is sometimes referred to as the book value or the net worth of the company. Since its value equals assets minus liability. Also Retained Earnings is a section under Equity. Retained earnings are the dollar amount of earnings reinvested back into the business.
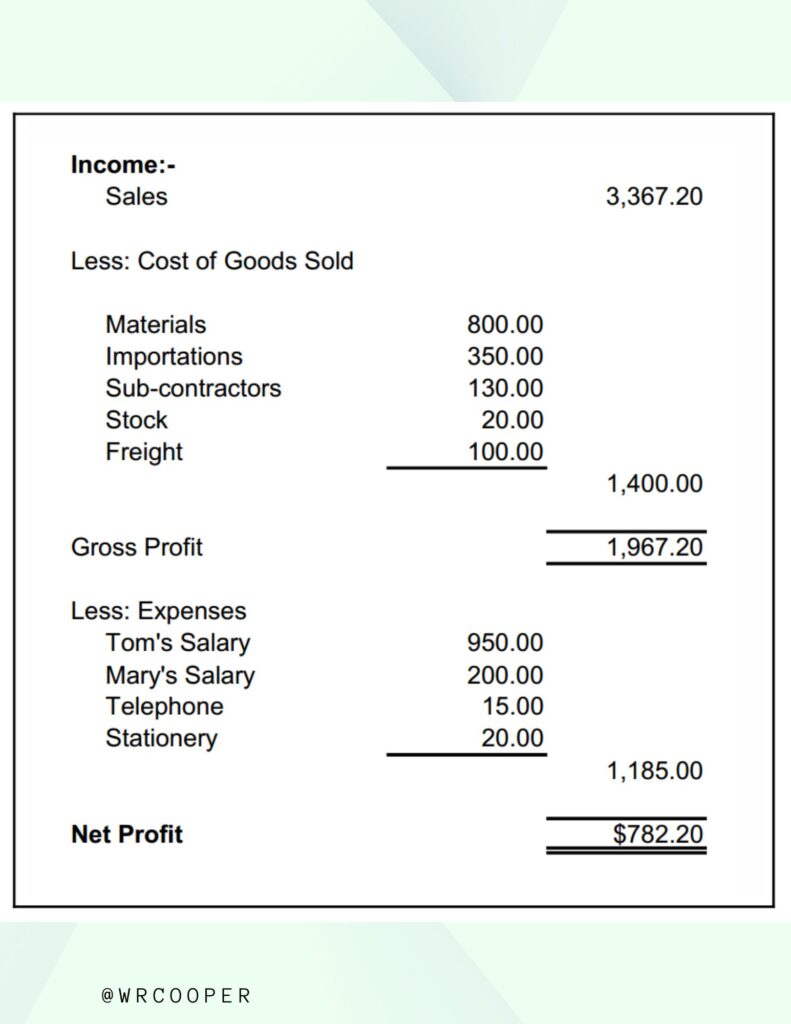
Alright, we’re making progress. Let’s look at the structure of an income statement.
The first component of an income statement is revenue, AKA The Top Line. It’s the dollar amount of products or services sold at a given time. The revenue section can be broken down further into specific types of income based on the products and services that are sold.
The next item is the cost of goods sold or cost of sale. These are the direct expenses associated with selling your product or your service, examples are inventory cost or labor.
The other expenses of the business are listed below gross profit, and the bottom line of the income statement is called net income. It’s the amount after subtracting all expenses of the business.
It answers the question: What is the profit or the loss of the business? Now let’s look at the structure of the cash flow statement.
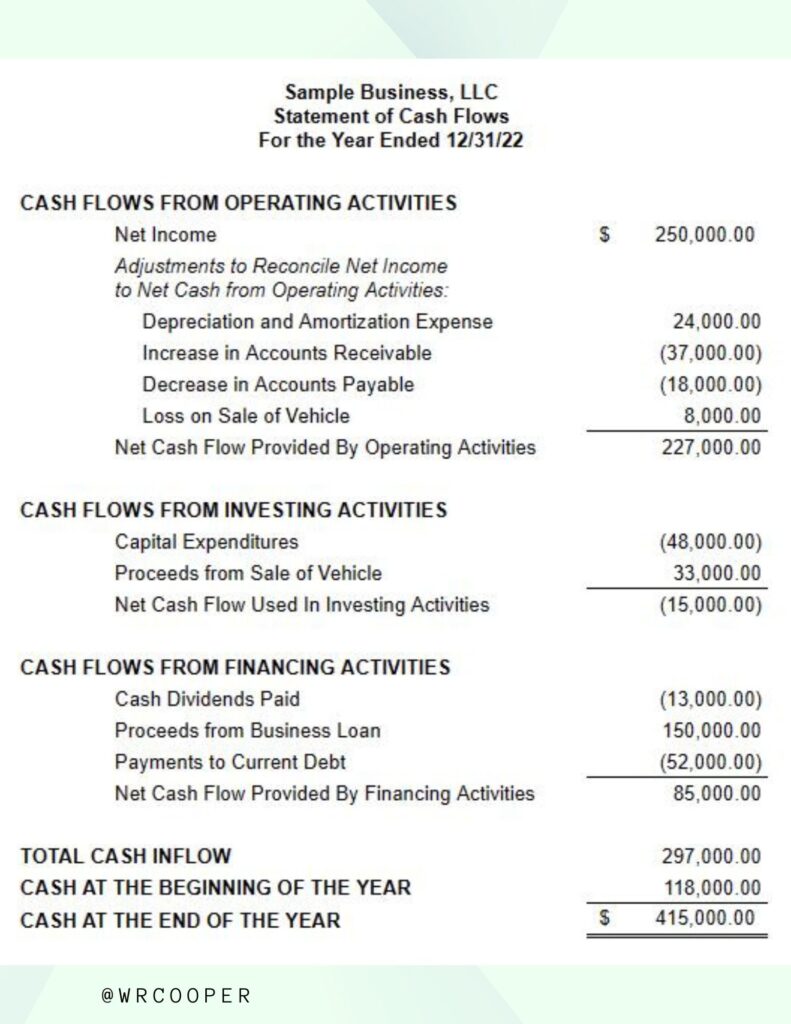
The cash flow statement tracks the cash coming in and out of the business. These cash inflows and outflows are broken into three categories: operating, financing, and investing cash flow.
Some operations are the cash activities related to performing the everyday regular ongoing activities of the business. Activities like selling products or services would be considered cash flow from operating activities.
Cash flow from financing relates to capital-raising activities of the business. When your business starts repaying the loan, that is considered a financing activity, and financing activities don’t just account for loans; they account for equity too. So if your business issues stock to investors, that is also a financing activity.
Cash flows from investing simply relates to the gains and losses from your business investments. When your business buys stock in another company, that is considered an investing activity. Now, the final step in the bookkeeping process.
Step 6: Make decisions based on the data
Remember, the purpose of bookkeeping is to help you make better, more profitable decisions. The balance sheet outlines your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, which means the balance sheet can be used to gauge the liquidity and sustainability of your business.
Let’s use an example of a company that has a million dollars in net income. Their balance sheet shows three months of income in accounts receivable. Knowing this information, the owner might decide to shorten the collection period to have more cash on hand.
The income statement tells you the operating performance of your company. It lists out the revenues and expenses and spits out a profit or a loss.
The cash flow statement tells you how much cash you have on hand. If your operating cash flow decreases, then you might reassess some of your operating expenses or even your pricing.
In short, bookkeeping can be the difference between you having a more profitable year this year than you had last year simply because you now have accurate data to make smarter decisions with.
Why choose WR Cooper?
We understand that bookkeeping process can be complicated. We are here to get your work done at fast pace and assist you to navigate these complex processes.
Conclusion:
In this article, we guided you about bookkeeping. You can also use QuickBooks and other accounting softwares for bookkeeping. Kindly share this article, it helps other business owners to see this article. We will you more information that helps you save on taxes and build your business. Stay tuned 😉
What is bookkeeping?
Bookkeeping is the recording of past financial data so that you can make future business decisions.
How do beginners learn bookkeeping?
Step 1: Gather Source documents
Step 2: Categorize your transactions
Step 3: Reconcile your transactions
Step 5: Read your financial statements
Step 4: Prepare financial statements
Step 6: Make decisions based on the data



